5co01 organisational performance and culture in practice
- October 13, 2022
- Posted by: Fletcher Samuel
- Category: CIPD Level 5

5CO01 is a unit that provides insights into the relationships between an organisation’s organisational structure and its commercial factors. It describes all of the modes and factors involved in delivering organisational change and performance. Learners must comprehend the organisational structures associated with:
- Importance of having a business strategy and planning in the digital environment
- Employee well-being is influenced by an appreciative culture.
Table of Contents
Learning objectives
Learners will be able to develop skills in the following areas:
- The relationship that exists between organizational structure, strategy, and the physical business environment.
- Analyze the factors and mode of external operations in order to assess an organization’s challenges and priorities.
- Explain theories and human behaviors in an organization, as well as the factors that cause change.
- Consider how to capitalize on diversity and inclusion to foster a positive culture.
- Examine the connection between an employee’s lifecycle and their job. Examine how people use organizational strategies to promote internal needs and achieve organizational goals.
The connection between organisational structure, strategies and physical environment
Learners will gain an understanding of how to assess the strengths and weaknesses of various organizational structures and why they should be supported. Different types of organizations have different products, services, and customers. They gain knowledge about evaluating the connections between organizational strategy, revenue generation methods, products, services, and customers. This can be accomplished by analyzing how external circumstances and business environments shape corporate organizational strategies, organizational perception and performance, strategy establishment and implementation, revenue-generating mode and methods of formulating strategies, and the concept of how to integrate strategies both horizontally and vertically.
Learners describe the mode and factors that have an impact on the external organization. This can be accomplished by employing reliable methods for analyzing legal regulations, the significance of the organizational lifecycle, and the market. Analyzing external factors influences organizational competitiveness and government policies. International and global factors, as well as international bodies, influence organizational decisions. When attempting to understand an organization’s external environment, demographics, social and technological insights, the importance of technology, and how trends affect an organization’s priorities are all important factors to consider.
Learners examine current organizational priorities, issues, and root causes. Organizational construction, differences in work sessions, and new products and services are examples of such priorities and issues. Other issues include working in a remote location, business expansion, financial targets, customer initiatives, reorganization, technology development, labor shortages, new product development, skill shortages, and restructuring.
The unit explains how people’s behaviors affect an organization’s structures and systems. It examines how people professionals can influence organizational structure and systems such as strategic influence, business partnerships, and organizational arrangement, staff capability, talent management, and identifying organizational priorities.
The unit evaluates the level of technology in an organization and how it affects work. Analyzing the functioning equipment, updating work systems in an organization, work systems, technology implementation across an organization, level of technological support, and organization technology spend can all be used to assess the level of technology.
Organisational culture and actual outlook of the way people behave at work
Learners gain understanding of how to interpret people’s and organizations’ behaviors. This can be accomplished by examining how people and organizations behave. For example, the model of behavior in team performance is evaluated in order to comprehend the organizational culture. System theories, nudge theory, and high-performance organizational theory are models that effectively explain different workplace cultures. Leadership and management, group dynamics, organizational support, and motivational theory all attempt to explain human and organizational behavior.
Learners assess the factors that drive change and how those changes are felt. There are several change management approaches, including Lewin’s three-step change model, Kotter’s eight-stage model, planned model of change, drivers of change, environmental model of change, and levers for change.
The unit describes how diversity and inclusion are implemented in the workplace to foster a positive culture. The concepts of diversity and inclusion are well defined while also outlining current diversity and inclusion legislation. The unit sheds light on the impact of culture in the absence of diversity and inclusion. Learners gain proficiency in assessing organizational culture and theory models, assessing the stages of culture in an organization, and outlining cultural classifications. Fair processes and policies, shared skills and knowledge, employee engagement, voice and involvement, shared beliefs, and organizational learning all contribute to a positive culture.
The impact of people practices on organizational culture and behavior determines how people behave at work. This can be determined by observing how much people practice influences people’s behavior. People can be champions for better work and better working lives, for example, by modeling their behavior through role models and policies. Furthermore, beliefs and values, trust, motivation when someone is rewarded, people attitudes toward provisions and learning, and the value an organization places on employees all influence the potential for impact.
The unit investigates the significance of employee well-being at work as well as the factors that influence well-being. This can be accomplished by assessing how employee well-being affects employee engagement, purpose at work and job satisfaction, motivation, physical and mental health, resilience, and self-status. These are all associated with: psychological work-life balance and family challenges; motivation, for example, expectancy theory, where employees put forth effort to perform in order to be rewarded; employee commitment level and issues arising from this such as punctuality, absenteeism, efficiency and capability, relationships stress and conflicts.
How people practice contributes to attaining organisational goals and objectives.
The unit assesses the overview of people’s practice roles at each stage of the lifecycle and how they progressively evolve while providing a firm evaluation of the relationship between employee lifecycle and work-life. Attraction, recruitment, induction, engagement, succession, exit, and post-employment connections are all components of the employee lifecycle.
People practices are related to organizational areas, such as helping others and implementing organizational strategies. This is accomplished by evaluating the links between specific areas of people practice such as human resources, learning and development, and other organizational aspects. The links between some regions of people practice and function making strategies, the links between people practices and organizational functions, the services provided by some regions of people practice and their support in an organization, and the methods by which strategies for people practice are acquired, employees, and organizational support
The unit outlines the current themes that define how people practice carrying out their work in specific areas. This is significant in terms of providing a solution to work challenges encountered in various work settings and environments. Learners examine how current insights shape people’s work in the internal and external environments.
Students will examine the processes of consulting and engaging with internal clients to better understand their needs. This is accomplished by conducting a consultation process to understand how people practices work on internal customer needs, caring out stakeholder analysis, conducting consultation and communication processes, and conducting an activity need analysis.
Learners will have the opportunity to discuss the critical components of project planning strategies that ensure project completion while meeting the needs of the customers. These components include planning, such as setting goals, milestones, assessing risks, gathering resources, costs, and interrelationships; project management, such as conception, development, realisation, and termination; and developing strategies to assist a project in meeting its requirements. For example, the leadership will communicate with stakeholders on a regular basis and will engage in activities that aid in monitoring and evaluation.
AC 1.1 Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of different types of organisation structures including the reasons underpinning them.
Prior to assessing the benefits and drawbacks of various organizational structures, it is critical to understand the concept and its application in the organization. Structure of the organization According to Maduenyi et al. (2015), organizational structure refers to how different organizational activities are carried out in order to achieve the firm’s goals and objectives. These activities may include enforcing the rules and assigning individual responsibilities. Organizational structure also includes how information flows between different levels of the organization. Flat and hierarchical structures are both common.
Hierarchical: This structure is described as a pyramid, with clear authority and levels within the company. Except for the chief executive officer, every individual in the company who follows this structure is a subordinate to another (CEO). Figure 1 illustrates an example of such a structure.
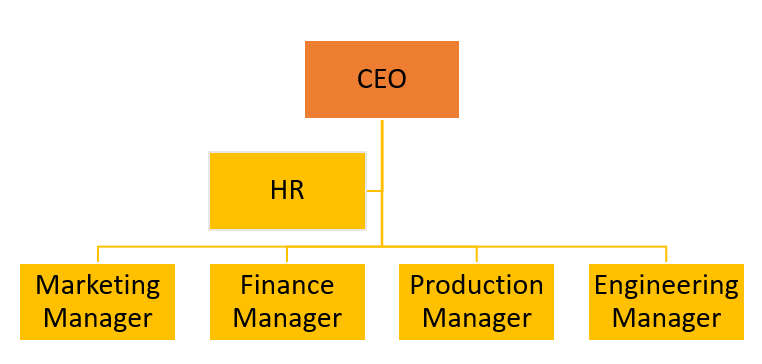
A flat organizational structure is in contrast to a hierarchical one. There are few or no levels between the leadership and management and the employees, as the name implies. This structure is distinguished by less supervision and employee involvement in decision making.
Table 1 summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of the two structures.
| Structure | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Hierarchical | -Employees participate in decision making.
-Few levels indicate a high level of coordination and communication. -Process of effective decision-making -Reduces the company’s budget. | -Confusion and power struggles are possible.
-Employees may be missing specific job roles. -It is only available to small businesses. |
| Flat | -Effective management and leadership.
-Opportunities for advancement are motivating. -Specialists are easily obtained. | -Communication that is ineffective.
-Departmental rivalry is a possibility. -Bureaucracy can have an impact on an organization’s innovativeness and performance. |
AC 1.2 Analyse connections between organisational strategy, revenue generation, products, services and outcomes.
Organizational strategy refers to the actions and activities that a company plans to take in order to achieve its goals and objectives. These actions constitute the strategic plan and necessitate extensive participation from all organizational departments and levels. According to Katuse (2021), organizational strategy is based on several factors such as resources, organizational goals, innovation, and employee learning and development. Corporate, business, and functional strategies are the three types of organizational strategies.
- Organisational Strategy and Revenue
The connection between strategy and revenue generation is centered on how businesses adapt to changes and establish priorities and directions. Outlining the business direction is part of organizational strategy. This ensures that the company meets its goals and maintains its competitiveness, as evidenced by high revenue. Furthermore, an organizational strategy ensures that the firm’s approaches and products are in line with the needs of its customers. This increases the firm’s market share, which increases revenue.
- Organisational Strategy and Products, Services, and Outcomes
The development of an organizational strategy entails the creation of a plan that ensures the firm adapts to current market trends and dynamics. Changing customer needs and preferences are among these trends. This implies the need for a wide range of products and services that not only meet the needs of customers but also align with future trends. For example, in the banking sector, the majority of companies are currently focusing on implementing information and communication technology (ICT) to improve service delivery. These approaches serve as the foundation for achieving business objectives. Another aspect of organizational strategy is the simplification and clarification of decision-making processes, which is critical in increasing profits and achieving the firm’s vision and goals. An effective organizational strategy is aligned with the goals and objectives of the company and ensures that all key performance indicators (KPIs) are met.
Struggling with Your CIPD?
Secure your future with our high-quality paper—order now!
You can talk to the writer using our messaging system and keep track of how your assignment is going.
Order Now WhatsAppAC 1.3 Analyse external factors and trends impacting organisations.
AC 1.4 Assess current organisational priorities and the associated issues and causes.
AC 1.5 Explain how people practices impact on organisational systems and structures.
AC 1.6 Evaluate the scale of technology within organisations and how it impacts work.
AC 3.3 Discuss key themes that currently shape the work of an area of people practice and how these impact on the provision of people solutions.
Video Summary
References
- CIPD, 2020. Organisation design. CIPD Factsheet. Available [online] at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/organisational-development/design-factsheet# [Accessed December 26, 2021].
- Katuse, P., 2021. Employee Perceptions on Organisational Strategy Implementation in Covid 19 Era. Indian Journal of Economics and Business, 20(3).
- Maduenyi, S., Oke, A.O., Fadeyi, O. and Ajagbe, A.M., 2015. Impact of organisational structure on organisational performance.
Related Articles:
Comments are closed.
