5CO02 Assignment Example
- November 1, 2022
- Posted by: Fletcher Samuel
- Category: CIPD Level 5

The 5CO02 Evidence-based Practice in the CIPD Level 5 course focuses on applying evidence-based practice to strengthen decision-making within HR and L&D. It enables learners to gather and analyse both quantitative and qualitative data to address real workplace challenges. The module also explores critical thinking, ethical considerations and methods for evaluating the impact of people practices on organisational outcomes. Developing these competencies not only enhances academic performance but also equips learners to handle real-world HR issues effectively.
Table of Contents
Task one
Learning Outcome 1: Gain a deep understanding of strategies that support critical thinking and the use of evidence to improve decision-making.
AC 1.1 Evaluate the concept of evidence-based practice (EBP) and provide two examples of where Technivara could use it to ensure sound decision-making in people practice.
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is a structured organisational decision-making approach grounded in critical thinking, systematic evaluation and the integration of multiple evidence sources, rather than assumptions, habits or personal preferences. It draws upon four core categories of evidence: internal organisational data, expert knowledge, stakeholder insights and relevant academic or industry research. The purpose of EBP is to ensure that decisions are reasonable, defensible and likely to generate positive outcomes (CIPD, 2023).
Strengths and Weaknesses
EBP reduces the likelihood of poor or biased decisions by basing choices on verifiable information rather than tradition. This is particularly valuable for Technivara, where Bill’s traditional leadership style and reliance on paper-based systems limit the depth and accuracy of insights available. Additionally, EBP enhances organisational credibility, as decisions grounded in robust evidence are more defensible to the board, employees and regulators, thereby supporting more confident strategic planning (CIPD, 2025).
However, gathering and analysing evidence can be time-consuming, potentially slowing decision-making in a fast-paced engineering environment (Alsadaan & Ramadan, 2025). Technivara’s outdated systems further complicate data extraction and analysis. Another limitation is the risk of bounded rationality, where decision-makers rely only on easily accessible or convenient evidence, leading to incomplete conclusions. In the absence of digitised HR data, Technivara may be especially vulnerable to this challenge (Alsadaan & Ramadan, 2025).
Ways Technivara Could Apply EBP
Planned Business Growth and Workforce Planning
As Technivara enters its sixteenth year, EBP can support decision-making on future workforce and skills needs. The organisation could analyse productivity data, turnover trends, skills gaps and industry research on emerging engineering competencies (VQ Solutions, 2025). When combined with managerial insight, this evidence would enable more informed recruitment, training and succession-planning strategies aligned with anticipated business growth.
Modernising People-Practice Systems and Processes
Sue has identified that the current paper-based processes reduce accuracy and expose the organisation to potential risks. Through EBP, Technivara could review internal error rates, processing times, employee feedback and best-practice research to determine whether transitioning to a digital HR information system would improve efficiency, accuracy and compliance (Cognizant, 2024). This approach would support a modernisation decision based on clear evidence rather than long-standing practices.
Struggling with Your CIPD?
Secure your future with our high-quality paper—order now!
You can talk to the writer using our messaging system and keep track of how your assignment is going.
Order Now WhatsAppAC 1.2 Evaluate one appropriate analysis tool and one appropriate analysis method that Technivara might apply to recognise and diagnose issues, challenges, and opportunities.
An analysis tool is a structured approach used to examine organisational problems, while an analysis method refers to the process of gathering or interpreting evidence. When combined, these approaches enable organisations to diagnose issues, identify opportunities and make evidence-based decisions.
Analysis Tool
Fishbone (Cause-and-Effect) Analysis
The Fishbone Analysis is a diagnostic technique used to identify the root causes of problems by categorising contributing factors into key groups such as processes, people, environment, technology and policies. It is particularly useful when issues are repetitive or complex (Sakdiyah, Eltivia & Afando, 2022).
Application at Technivara
Technivara still relies on paper-based and outdated people-practice systems, which Sue notes result in weak data capture and risky decision-making. The Fishbone tool could help uncover the root causes of challenges such as slow recruitment processes or inaccurate HR records. By mapping contributing factors—including resistance to change, lack of digital systems, insufficient staff training and fragmented processes under Bill’s leadership—Technivara would gain clarity on what drives inefficiency and where improvements can be made.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Fishbone Analysis provides a clear visual representation of the full range of potential causes behind complex people-practice issues, supporting Sue in presenting a structured, evidence-driven case to Bill and the board (ASQ, 2024). It also promotes teamwork, as cross-functional brainstorming encourages knowledge-sharing and collaborative problem solving (Channell, 2021).
However, the quality of the analysis depends heavily on participant expertise. Limited knowledge or bias may lead the team to overlook key root causes (BGMC, 2023). Additionally, the tool does not prioritise factors, meaning Technivara may identify numerous issues but still require further analysis to determine which ones matter most.
Analysis Method
Interviews
Interviews involve gathering qualitative data through structured or semi-structured conversations with employees or stakeholders (Barber, 2024).
Application at Technivara
As the organisation prepares for expansion, Sue needs deeper insights into employee experiences, skills gaps, process inefficiencies and potential cultural barriers. Interviews with employees, line managers and senior leaders could reveal challenges such as inconsistent onboarding, reluctance to adopt new processes, limited data literacy or concerns about increased workloads. They may also highlight opportunities, such as staff willingness to embrace new technologies or suggestions for enhancing workflow efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Interviews provide rich, in-depth evidence on employee motivations, challenges and lived experiences, information that cannot be captured through paper records alone. They also strengthen trust and engagement, demonstrating that employee voice is valued during a period of organisational change (Reddy, 2019).
However, interviews can be time-consuming to conduct and analyse, which can strain a small people-practice team already using outdated systems (Reddy, 2019). They are also vulnerable to bias, as interviewees may tailor their responses to please management or avoid conflict, especially in a traditional culture shaped by Bill’s leadership.
AC 1.3 Explain the main principles of critical thinking including how these might apply to your own and others’ ideas to assist objective and rational debate at Technivara
Critical thinking is the structured process of analysing, evaluating and reflecting on information to make well-reasoned, objective judgements. It involves questioning, seeking evidence and thinking carefully before making decisions (CIPD, 2019). At Technivara, critical thinking is essential to ensure that decisions about people practices, training and organisational change are logical, evidence-based and aligned with strategic goals. Key principles of critical thinking include:
Unbiased and Logical Analysis
This principle involves separating facts from opinions, and avoiding personal preferences or long-standing organisational traditions when making decisions. It requires fair, systematic evaluation of arguments, identifying cause-and-effect relationships and avoiding emotional reasoning or assumptions (The Foundation for Critical Thinking, 2019).
Questioning and Validating Evidence
Critical thinkers assess the relevance, credibility and reliability of the evidence they use. This includes checking sources, comparing data from different places and identifying gaps or inconsistencies. The aim is to ensure conclusions are built on strong information, not anecdotal or biased observations (Psychology Town, 2024).
Awareness of Bias
This principle focuses on recognising both conscious and unconscious biases in oneself and others. It involves reflecting on personal assumptions, departmental interests and elements of organisational culture that may influence reasoning (Steele, 2024).
Application to My Own Ideas
Applying objective and rational analysis to my own ideas at Technivara ensures recommendations are based on evidence rather than assumptions. For example, when suggesting the adoption of a digital HR system, I would consider employee feedback, error rates in current processes and industry best practice before making a proposal. Focusing on reliable information would enable me to present a clear, evidence-based case to the board while minimising personal bias.
Application to Others’ Ideas
Awareness of bias also helps evaluate colleagues’ ideas fairly. For instance, if a line manager wants to continue using paper-based HR processes simply because it has always been the norm, recognising their attachment to tradition allows me to challenge this gently and encourage an evidence-based discussion. Being conscious of potential biases helps ensure that all suggestions are judged on their merit, supporting stronger and more informed decision-making.
AC 1.4 Explain two decision-making processes that Technivara could apply to ensure that effective outcomes are achieved.
Effective decision-making processes can help People Practitioners at Technivara address people-related challenges such as outdated systems, skills shortages and resistance to change. De Bono’s Six Thinking Hats and Action Learning are two suitable approaches that can support better decisions in this environment.
De Bono’s Six Thinking Hats
De Bono’s Six Thinking Hats is a structured decision-making model in which individuals or teams explore an issue through six different perspectives: facts (white), emotions (red), risks (black), benefits (yellow), creativity (green) and process control (blue) (The Decision Lab, 2025). These different thinking styles prevent discussions from being dominated by personal preferences or habitual ways of working (The De Bono Group, 2019).
Application at Technivara
A major area of debate at Technivara is the shift from paper-based systems to digital HR processes. By applying the Six Hats approach, the People Practice team can examine this issue more thoroughly:
- White Hat: current error rates, processing times and compliance risks
- Black Hat: costs, implementation challenges and employee resistance
- Yellow Hat: improved accuracy, better decision-making and stronger reporting
- Green Hat: new workflow ideas or innovative onboarding tools
- Red Hat: employee feelings and attitudes toward digital change
- Blue Hat: structuring and managing the decision-making process
This creates a more balanced and comprehensive evaluation, combining logic, emotion, risk, creativity and structure (The Decision Lab, 2025).
Benefits and Drawbacks
The model reduces bias and conflict—helpful in Technivara’s traditional culture under Bill’s leadership. It also encourages deeper exploration of all aspects of a people-practice issue (The Decision Lab, 2025).
However, it requires skilled facilitation to keep discussions on track, and it may be time-consuming in a busy engineering organisation (The De Bono Group, 2019).
Action Learning
Action Learning involves small groups working together on real organisational problems, asking questions, challenging assumptions and reflecting on potential solutions. It supports learning while solving practical issues (CFI, 2022).
Application at Technivara
Technivara could form an Action Learning set to address challenges such as long recruitment timelines or gaps in workforce planning. A group made up of HR, engineering, operations and management staff could examine root causes of delays, test solutions—such as simplified job approval workflows—and reflect on what works in practice. This encourages continuous improvement and shared decision-making (CFI, 2022).
Benefits and Drawbacks
Action Learning produces practical, evidence-based solutions that improve people-practice processes. It also builds teamwork and capability, helping shift the organisation toward a more modern working culture (Barry, 2024).
However, it requires regular participation, which may be difficult during busy growth periods (Király & Dén-Nagy, 2024). In addition, outcomes depend heavily on the group’s ability to reflect and learn effectively.
AC 1.5 Assess two different ethical perspectives including how these could be used at Technivara to inform and influence decision-making.
Ethical perspectives provide principles that help organisations make morally sound decisions. For Technivara, utilitarianism and deontological (Kantian) ethics are two relevant frameworks. Examining these perspectives shows how they influence decision-making, shape behaviour and contribute to organisational culture.
Utilitarianism
Utilitarianism suggests that an ethical action is one that produces the greatest good or happiness for the largest number of people. It is a practical approach to workplace decision-making because it focuses on outcomes rather than rules (Wooldridge, 2019).
Impact on Decision-Making at Technivara
Using a utilitarian approach, Technivara should prioritise decisions that maximise long-term value for employees, customers and the organisation. For example, replacing paper-based HR systems with digital ones may involve short-term challenges—training costs, disruptions and resistance. However, if digitalisation leads to greater accuracy, faster operations and better business growth, utilitarianism would consider it the ethically preferable choice.
This theory may also guide workforce planning decisions (Layne, 2024). If introducing structured career development improves employee engagement, reduces turnover and enhances productivity for most employees, such a decision would be ethically justified from a utilitarian perspective.
Assessment
Utilitarianism supports future-oriented decisions that promote overall organisational benefit, which can help Sue advocate for modernisation. However, it may overlook the needs of individuals who experience negative impacts, such as employees anxious about new technologies, unless strong support systems are put in place (Wooldridge, 2019).
Deontological (Kantian) Ethics
Deontological ethics emphasises duties, rules and moral principles. According to this perspective, an action is ethical if it respects individuals, upholds moral standards and does not exploit or harm people, regardless of the outcome. It prioritises fairness, honesty and respect (Radford University, 2025).
Impact on Decision-Making at Technivara
Applying this perspective at Technivara means ensuring fairness and consistency in all decisions. For instance, the organisation would commit to transparent procedures and respectful treatment of employees during performance or capability processes, even if shortcuts could save time. A deontological approach would also promote merit-based recruitment during business expansion, rather than decisions based on convenience or personal preference (Holmer, 2021).
Assessment
Deontological ethics can strengthen trust, support ethical leadership and foster a positive culture element Technivara needs during its modernisation journey. However, strict adherence to rules may reduce flexibility, slow decision-making or limit responsiveness in a fast-paced engineering environment (Radford University, 2025).
Learning Outcome 3 :Learn how to measure the impact of people-focused practices on an organization.
AC 3.1 Appraise two different ways that Technivara could measure financial and non-financial performance, providing one example of each.
Performance measurement enables Technivara to assess its organisational health, effectiveness and readiness for future growth. By examining both financial and non-financial indicators, the company can gain insights into profitability, operational efficiency, employee experience and customer outcomes. Two suitable approaches are Return on Investment (ROI) for financial performance and the Balanced Scorecard for non-financial performance.
Financial Performance Measure: Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI evaluates how effectively an investment generates returns relative to its cost. It helps organisations assess the value and effectiveness of financial decisions and compare different investment options (Corporate Finance Institute, 2025). ROI is particularly relevant for a growing organisation like Technivara, where the board must justify expenditure as the business expands.
Technivara Application Example
If Technivara were to implement a digital HR information system to replace its paper-based processes, ROI could determine whether the investment delivers financial value. The organisation would compare the cost of purchasing and installing the system with the savings achieved through reduced administrative hours, fewer manual errors and improved reporting accuracy. A positive ROI would demonstrate that the investment supports long-term financial performance and scalable growth (Stone X, 2025).
Appraisal
ROI is a clear and measurable indicator that allows Technivara to evaluate the financial benefits of modernisation initiatives. It helps build evidence-based business cases and reduces the risk of spending on tools that do not deliver adequate returns (Stobierski, 2020). However, ROI does not easily capture intangible benefits such as improved morale or stronger compliance unless these are converted into monetary values, something difficult to achieve due to the organisation’s limited data (Stone X, 2025).
Non-Financial Performance Indicator: Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard measures organisational performance across four perspectives, financial, customer, internal processes and learning and growth, creating a holistic view of success. It is especially useful for identifying non-financial drivers that support long-term performance (Hayes, 2025).
Technivara Application Example
Technivara could use the Balanced Scorecard to track employee satisfaction, process efficiency, training effectiveness and customer experience in the electronics and medical industries (Hayes, 2025). For example, it could monitor the percentage of HR processes completed on time or gather employee feedback on onboarding, providing valuable insight into people-practice effectiveness and future capability needs.
Appraisal
The Balanced Scorecard enables Technivara to evaluate performance beyond financial outcomes, giving a broader understanding of organisational strengths and weaknesses. However, it relies on accurate data collection, which is currently hindered by the company’s reliance on paper-based systems. Improvements in data capture and digitalisation would therefore be necessary for effective use of the tool (Francis, 2025).
AC 3.2 Explain how people practices could add value at Technivara and identify two methods that might be used to measure the impact of these people practices.
People practices add value when they enhance organisational performance, improve the employee experience and support the achievement of strategic goals. This value may be monetary (such as reduced turnover costs and increased productivity) or non-monetary (such as improved engagement, stronger organisational culture and enhanced compliance) (Mowles, 2021). Within Technivara, people practices can support the organisation’s modernisation efforts, enable better decision-making and build the capacity needed for future expansion.
How People Practice Adds Value to Technivara
Enhancing efficiency and accuracy across the organisation
Technivara currently relies on outdated, paper-based HR processes. Modernising these practices such as digitising employee records, streamlining recruitment processes and automating reporting adds value by reducing administrative time, minimising errors and enabling faster, more informed decision-making. These improvements support the company’s strategic expansion plans while reducing operational risks (Lawler & Boudreau, 2020).
Improving employee capability and commitment
Targeted learning and development initiatives, improved onboarding and structured performance management help employees build the skills required for an expanding engineering and manufacturing environment. When employees see opportunities for growth, they feel supported and are more likely to stay. This improves retention, reduces recruitment costs and boosts productivity, critical value drivers in a highly technical industry (Lawler & Boudreau, 2020).
Two Ways to Measure the Impact of People Practice
Cost–Benefit Analysis (CBA)
CBA compares the financial benefits of a people initiative with its associated costs (Schmidt, 2024). For example, if Technivara were to implement a digital HR information system, CBA could measure benefits such as reduced administrative hours, fewer compliance errors and shorter recruitment timelines against the cost of system implementation. This method provides a clear financial justification for investment and helps the board assess whether initiatives generate measurable value (EBSCO, 2021).
Employee Engagement and Satisfaction Surveys
These surveys capture non-financial value by measuring employees’ perceptions of onboarding, communication, leadership quality and development opportunities (Miller, 2020). For Technivara, post-implementation surveys following new HR processes or training programmes can reveal whether morale has improved, whether employees are confident using new systems or whether further support is needed. High engagement levels are often linked to lower turnover, increased productivity and greater innovation, strong indicators of long-term organisational value (REBA, 2025).
1009 Words
Task two
Learning Outcome 2: Recognize the importance of ethical decision-making and develop ways to address challenges in people management within the workplace.
AC 2.1 Table 1 shows Technivara’s turnover and recruitment data for 2024. Sue has asked you to convert the data into percentage form, for each of the departments, to show:
- leavers as a % of the total number of employees
- vacancies as % of the total number of employees
- positions filled as a % of the total number of employees
| Total in Department 2024 | Leavers for 2024 | Leavers as a % against total in each Department | Positions Vacant | Vacancies as a % against total in each Department | Positions filled | Positions filled as a % of total in each Department | |
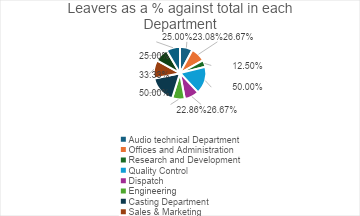
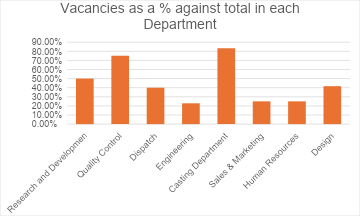
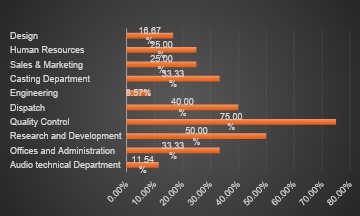
| Audio technical Department | 26 | 6 | 23.08% | 8 | 30.77% | 3 | 11.54% |
| Offices and Administration | 15 | 4 | 26.67% | 5 | 33.33% | 5 | 33.33% |
| Research and Development | 8 | 1 | 12.50% | 4 | 50.00% | 4 | 50.00% |
| Quality Control | 4 | 2 | 50.00% | 3 | 75.00% | 3 | 75.00% |
| Dispatch | 15 | 4 | 26.67% | 6 | 40.00% | 6 | 40.00% |
| Engineering | 35 | 8 | 22.86% | 8 | 22.86% | 3 | 8.57% |
| Casting Department | 6 | 3 | 50.00% | 5 | 83.33% | 2 | 33.33% |
| Sales & Marketing | 12 | 4 | 33.33% | 3 | 25.00% | 3 | 25.00% |
| Human Resources | 4 | 1 | 25.00% | 1 | 25.00% | 1 | 25.00% |
| Design | 12 | 3 | 25.00% | 5 | 41.67% | 2 | 16.67% |
AC 2.2 When you have completed Table 1, present your findings using a minimum of three different types of diagrammatical forms.
Leavers as a percentage against total in each department
Vacancies as a % against total in each Department
Positions filled as a % of total in each Department
AC 2.3 Table 2 contains evaluation feedback from 42 employees who attended a recent learning and development activity. Sue would like you to review the feedback and identify patterns, themes or trends that might be occurring and make recommendations based on your findings.
The feedback from the evaluation of the 42 employees who participated in Technivara’s latest learning and development (L&D) programme provides insight into which activities were successful and which require improvement. Analysing quantitative data allows the identification of patterns, themes, and trends that can guide future L&D initiatives and ensure alignment with organisational objectives.
Patterns Observed
Pattern 1: High satisfaction with facilitator competence and resources
Most employees rated the facilitator and materials positively:
- Awareness of the subject: 39 out of 42 positive responses (13 strongly agree, 26 agree)
- Facilitation clarity: 33 affirmative responses
- Quality of resources: 36 positive responses, with no disagreement
This indicates that the choice of trainer and training materials was effective and well-received. Technical delivery did not hinder learning (CIPD, 2024).
Pattern 2: Low alignment with performance outcomes
Responses regarding learning outcomes and skill application were much lower:
- Learning outcomes achieved: 5 positive responses, 33 negative responses
- Skills applicability to role: 6 positive, 14 disagree, 6 strongly disagree
- Connection to performance targets: 6 positive, 12 disagree, 11 not sure
This shows a significant gap between the training content and its relevance to employees’ job roles and performance standards (Pappas, 2022).
Themes Identified
Theme 1: Lack of learner involvement and engagement
Interactive engagement levels were low: 32 employees disagreed or strongly disagreed that they participated actively. This suggests the session may have been over-facilitated, leaving insufficient opportunity for learners to explore material, ask questions, or contextualise learning, which can hinder knowledge transfer (Jerab, 2024).
Theme 2: Low consideration of personal learning needs
The lowest-scoring statement showed that individual learning preferences were largely ignored: 18 respondents were unsure, 14 disagreed, and only 10 felt their needs were considered. This indicates a generic training design, with minimal adaptation to different learning styles, job roles, or team settings (OPM, 2018).
Trends Observed
Trend 1: Positivity focused at the start of training
Employees reported high satisfaction at the beginning (clear goals, good resources) but dissatisfaction increased by the end (learning outcomes achieved, applicability). This indicates that delivery quality was high, but practical effectiveness was low (DigitalDefynd, 2024).
Trend 2: Decline in perceived value
Negative responses increased as questions focused on application, impact, and alignment to work. This shows that the L&D activity was not well integrated into workplace performance or organisational growth objectives (O’Donnellan, 2023).
Recommendations
Recommendation 1: Conduct a Training Needs Analysis (TNA) prior to programme design
A structured TNA will help identify job demands, performance gaps, team priorities, and learner preferences.
- Benefits: Ensures content is relevant to roles and performance objectives, improving uptake and motivation (Pappas, 2022).
- Risks: TNA is time-consuming and may delay training delivery; incomplete information may occur due to current paper-based HR systems (Jerab, 2024).
- Financial Implications: Short-term costs increase for surveys, interviews, and analysis, but long-term savings arise from more focused training and reduced turnover (OPM, 2018).
Recommendation 2: Redesign sessions to increase interaction and workplace application
Training should incorporate interactive activities (e.g., group discussions, case studies, simulations, Q&A) and practical tasks aligned with workplace application.
- Benefits: Interactive learning enhances retention, encourages practical application, and strengthens the connection between training and performance (CIPD, 2024).
- Risks: Traditional leaders may resist experiential learning (Brassey, 2019). Facilitators may require additional training (Christensen, 2019). Not all trainers may be skilled in experiential techniques (van Dam, 2019).
- Financial Implications: Initial investment for materials, scenario creation, and facilitator training is required. Effective skill application is likely to improve organisational performance (DigitalDefynd, 2024). Improved workplace application is expected to increase measurable performance (O’Donnellan, 2023).
Conclusion
The evaluation shows that Technivara’s L&D sessions were well delivered but lacked relevance, interactivity, and alignment with workplace application. Implementing a Training Needs Analysis and redesigning sessions to be more interactive and performance-oriented will enhance employee capability, improve ROI, and support the company’s modernisation and growth objectives.
Related Articles:
